
|
在上一篇文章中我们已经接触到了protect这个关键字的作用了,今天我们继续深入继承的深入学习。 一、三种继承方式: 1、从问题引出主题: (1)冒号( class Parent 表示继承关系,Parent表示被继承的类,public的意义是什么? 表示继承关系,Parent表示被继承的类,public的意义是什么?{ }; class Child : public Parent { } (2)是否可以将继承语句中的public换成protected或者说private,因为写代码的时候,你肯定会有这样的好奇心;同时如果可以这样写的话,那么,这样与public继承又有什么区别呢?咋们还是通过实际代码来理解: #include <iostream>#include <string> using namespace std; class Parent { }; class Child_A : public Parent { }; class Child_B : protected Parent { }; class Child_C : private Parent { }; int main() { return 0; } 试试看,能否编译通过: root@txp-virtual-machine:/home/txp# vim test.cpproot@txp-virtual-machine:/home/txp# g++ test.cpp root@txp-virtual-machine:/home/txp# 注解:通过编译我们发现,完全没有毛病。 2、c++中支持三种不同的基础方式
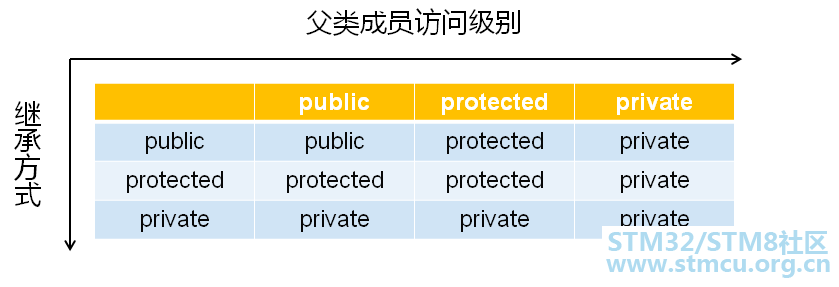
继承成员的访问属性: =Max{继承方式,父类成员访问属性} 注意:c++中的默认继承方式为private 代码实践: #include <iostream>#include <string> using namespace std; class Parent { protected: int m_a; protected: int m_b; public: int m_c; void set(int a, int b, int c) { m_a = a; m_b = b; m_c = c; } }; class Child_A : public Parent { public: void print() { cout << "m_a" << m_a << endl; cout << "m_b" << m_b << endl; cout << "m_c" << m_c << endl; } }; class Child_B : protected Parent { public: void print() { cout << "m_a" << m_a << endl; cout << "m_b" << m_b << endl; cout << "m_c" << m_c << endl; } }; class Child_C : private Parent { public: void print() { cout << "m_a" << m_a << endl; cout << "m_b" << m_b << endl; cout << "m_c" << m_c << endl; } }; int main() { Child_A a; Child_B b; Child_C c; a.m_c = 100; // b.m_c = 100; // Child_B 保护继承自 Parent, 所以所有的 public 成员全部变成了 protected 成员, 因此外界无法访问 // c.m_c = 100; // Child_C 私有继承自 Parent, 所以所有的成员全部变成了 private 成员, 因此外界无法访问 a.set(1, 1, 1); // b.set(2, 2, 2); // c.set(3, 3, 3); a.print(); b.print(); c.print(); return 0; } 输出结果: root@txp-virtual-machine:/home/txp# ./a.outm_a1 m_b1 m_c1 m_a4197200 m_b0 m_c4196272 m_a-903133344 m_b32766 m_c0 代码实践二: #include <iostream>#include <string> using namespace std; class Parent { protected: int m_a; protected: int m_b; public: int m_c; void set(int a, int b, int c) { m_a = a; m_b = b; m_c = c; } }; class Child_A : public Parent { public: void print() { cout << "m_a" << m_a << endl; cout << "m_b" << m_b << endl; cout << "m_c" << m_c << endl; } }; class Child_B : protected Parent { public: void print() { cout << "m_a" << m_a << endl; cout << "m_b" << m_b << endl; cout << "m_c" << m_c << endl; } }; class Child_C : private Parent { public: void print() { cout << "m_a" << m_a << endl; cout << "m_b" << m_b << endl; cout << "m_c" << m_c << endl; } }; int main() { Child_A a; Child_B b; Child_C c; a.m_c = 100; b.m_c = 100; // Child_B 保护继承自 Parent, 所以所有的 public 成员全部变成了 protected 成员, 因此外界无法访问 c.m_c = 100; // Child_C 私有继承自 Parent, 所以所有的成员全部变成了 private 成员, 因此外界无法访问 a.set(1, 1, 1); b.set(2, 2, 2); c.set(3, 3, 3); a.print(); b.print(); c.print(); return 0; } 输出结果: root@txp-virtual-machine:/home/txp# g++ test.cpptest.cpp: In function ‘int main()’: test.cpp:13:9: error: ‘int Parent::m_c’ is inaccessible int m_c; ^ test.cpp:63:7: error: within this context b.m_c = 100; // Child_B 保护继承自 Parent, 所以所有的 public 成员全部变成了 protected 成员, 因此外界无法访问 ^ test.cpp:13:9: error: ‘int Parent::m_c’ is inaccessible int m_c; ^ test.cpp:64:7: error: within this context c.m_c = 100; // Child_C 私有继承自 Parent, 所以所有的成员全部变成了 private 成员, 因此外界无法访问 ^ test.cpp:15:10: error: ‘void Parent::set(int, int, int)’ is inaccessible void set(int a, int b, int c) ^ test.cpp:67:18: error: within this context b.set(2, 2, 2); ^ test.cpp:67:18: error: ‘Parent’ is not an accessible base of ‘Child_B’ test.cpp:15:10: error: ‘void Parent::set(int, int, int)’ is inaccessible void set(int a, int b, int c) ^ test.cpp:68:18: error: within this context c.set(3, 3, 3); ^ test.cpp:68:18: error: ‘Parent’ is not an accessible base of ‘Child_C’ 注解:当子类定义的对象,如果继承关系不是public,那么子类定义的对象,就无法访问父类中的属性和方法了。 3、遗憾的事实
二、总结
好了,今天的分享就到这里,如果文章中有错误或者不理解的地方,可以交流互动,一起进步。 |
 微信公众号
微信公众号
 手机版
手机版
