特别说明:完整45期数字信号处理教程,原创高性能示波器代码全开源地址:链接
第8章 BasicMathFunctions的使用(一)
本期教程开始学习ARM官方的DSP库,这里我们先从基本数学函数开始。本期教程主要讲绝对值,加法,点乘和乘法四种运算。 8.1 绝对值(Vector Absolute Value) 8.2 求和(Vector Addition) 8.3 点乘(Vector Dot Product) 8.4 乘法(Vector Multiplication)
8.1 绝对值(Vector Absolute Value) 这部分函数主要用于求绝对值,公式描述如下: pDst[n] = abs(pSrc[n]), 0 <= n < blockSize. 特别注意,这部分函数支持目标指针和源指针指向相同的缓冲区。 8.1.1 arm_abs_f32 这个函数用于求32位浮点数的绝对值,源代码分析如下: - /**
- * @brief Floating-point vector absolute value. (1)
- * @param[in] *pSrc points to the input buffer
- * @param[out] *pDst points to the output buffer
- * @param[in] blockSize number of samples in each vector
- * @return none.
- */
-
- void arm_abs_f32( (2)
- float32_t * pSrc,
- float32_t * pDst,
- uint32_t blockSize)
- {
- uint32_t blkCnt; /* loop counter */
-
- #ifndef ARM_MATH_CM0_FAMILY (3)
-
- /* Run the below code for Cortex-M4 and Cortex-M3 */
- float32_t in1, in2, in3, in4; /* temporary variables */
-
- /*loop Unrolling */
- blkCnt = blockSize >> 2u; (4)
-
- /* First part of the processing with loop unrolling. Compute 4 outputs at a time.
- ** a second loop below computes the remaining 1 to 3 samples. */
- while(blkCnt > 0u)
- {
- /* C = |A| */
- /* Calculate absolute and then store the results in the destination buffer. */
- /* read sample from source */
- in1 = *pSrc;
- in2 = *(pSrc + 1);
- in3 = *(pSrc + 2);
-
- /* find absolute value */
- in1 = fabsf(in1); (5)
-
- /* read sample from source */
- in4 = *(pSrc + 3);
-
- /* find absolute value */
- in2 = fabsf(in2);
-
- /* read sample from source */
- *pDst = in1;
-
- /* find absolute value */
- in3 = fabsf(in3);
-
- /* find absolute value */
- in4 = fabsf(in4);
-
- /* store result to destination */
- *(pDst + 1) = in2;
-
- /* store result to destination */
- *(pDst + 2) = in3;
-
- /* store result to destination */
- *(pDst + 3) = in4;
-
-
- /* Update source pointer to process next sampels */ (6)
- pSrc += 4u;
-
- /* Update destination pointer to process next sampels */
- pDst += 4u;
-
- /* Decrement the loop counter */
- blkCnt--;
- }
-
- /* If the blockSize is not a multiple of 4, compute any remaining output samples here.
- ** No loop unrolling is used. */
- blkCnt = blockSize % 0x4u;
-
- #else (7)
-
- /* Run the below code for Cortex-M0 */
-
- /* Initialize blkCnt with number of samples */
- blkCnt = blockSize;
-
- #endif /* #ifndef ARM_MATH_CM0_FAMILY */
-
- while(blkCnt > 0u) (8)
- {
- /* C = |A| */
- /* Calculate absolute and then store the results in the destination buffer. */
- *pDst++ = fabsf(*pSrc++);
-
- /* Decrement the loop counter */
- blkCnt--;
- }
- }
1. 在这里简单的跟大家介绍一下DSP库中函数的通用格式,后面就不再赘述了。 (1) 基本所有的函数都是可重入的。 (2) 大部分函数都支持一组数的计算,比如这个函数arm_abs_f32就可以计算一组数的绝对值。所以如果只是就几个数的绝对值,用这个库函数就没有什么优势了。 (3) 库函数基本是CM0,CM3和CM4都支持的(最新的DSP库已经添加CM7的支持)。 (4) 每组数据基本上都是以4个数为一个单位进行计算,不够四个再单独计算。 (5) 大部分函数都是配有f32,Q31,Q15和Q7四种格式。 2. 函数参数,支持输入一个数组进行计算绝对值。 3. 这部分代码是用于CM3和CM4内核。 4. 左移两位从而实现每4个数据为一组进行计算。 5. fabsf:这个函数不是用Cortex-M4F支持的DSP指令实现的,而是用C语言实现的,这个函数是被MDK封装起来的。 6. 切换到下一组数据。 7. 这部分代码用于CM0. 8. 用于不够4个数据的计算或者CM0内核。 8.1.2 arm_abs_q31 这个函数用于求32位定点数的绝对值,源代码分析如下: - /**
- * @brief Q31 vector absolute value.
- * @param[in] *pSrc points to the input buffer
- * @param[out] *pDst points to the output buffer
- * @param[in] blockSize number of samples in each vector
- * @return none.
- *
- * <b>Scaling and Overflow Behavior:</b> (1)
- * \par
- * The function uses saturating arithmetic.
- * The Q31 value -1 (0x80000000) will be saturated to the maximum allowable positive value 0x7FFFFFFF.
- */
-
- void arm_abs_q31(
- q31_t * pSrc,
- q31_t * pDst,
- uint32_t blockSize)
- {
- uint32_t blkCnt; /* loop counter */
- q31_t in; /* Input value */
-
- #ifndef ARM_MATH_CM0_FAMILY
-
- /* Run the below code for Cortex-M4 and Cortex-M3 */
- q31_t in1, in2, in3, in4;
-
- /*loop Unrolling */
- blkCnt = blockSize >> 2u;
-
- /* First part of the processing with loop unrolling. Compute 4 outputs at a time.
- ** a second loop below computes the remaining 1 to 3 samples. */
- while(blkCnt > 0u)
- {
- /* C = |A| */
- /* Calculate absolute of input (if -1 then saturated to 0x7fffffff) and then store the results in the destination buffer. */
- in1 = *pSrc++;
- in2 = *pSrc++;
- in3 = *pSrc++;
- in4 = *pSrc++;
-
- *pDst++ = (in1 > 0) ? in1 : (q31_t)__QSUB(0, in1); (2)
- *pDst++ = (in2 > 0) ? in2 : (q31_t)__QSUB(0, in2);
- *pDst++ = (in3 > 0) ? in3 : (q31_t)__QSUB(0, in3);
- *pDst++ = (in4 > 0) ? in4 : (q31_t)__QSUB(0, in4);
-
- /* Decrement the loop counter */
- blkCnt--;
- }
-
- /* If the blockSize is not a multiple of 4, compute any remaining output samples here.
- ** No loop unrolling is used. */
- blkCnt = blockSize % 0x4u;
-
- #else
-
- /* Run the below code for Cortex-M0 */
-
- /* Initialize blkCnt with number of samples */
- blkCnt = blockSize;
-
- #endif /* #ifndef ARM_MATH_CM0_FAMILY */
-
- while(blkCnt > 0u)
- {
- /* C = |A| */
- /* Calculate absolute value of the input (if -1 then saturated to 0x7fffffff) and then store the results in the destination buffer. */
- in = *pSrc++;
- *pDst++ = (in > 0) ? in : ((in == INT32_MIN) ? INT32_MAX : -in);
-
- /* Decrement the loop counter */
- blkCnt--;
- }
-
- }
1. 这个函数使用了饱和运算,其实不光这个函数,后面很多函数都是使用了饱和运算的,关于什么是饱和运算,大家看Cortex-M3权威指南中文版的4.3.6 小节:汇编语言:饱和运算即可。 对于Q31格式的数据,饱和运算会使得数据0x80000000变成0x7fffffff(这个数比较特殊,算是特殊处理,记住即可)。 2. 这里重点说一下函数__QSUB,其实这个函数算是Cortex-M4/M3的一个指令,用于实现饱和减法。 比如函数:__QSUB(0, in1) 的作用就是实现0 – in1并返回结果。这里__QSUB实现的是32位数的饱和减法。还有__QSUB16和__QSUB8实现的是16位和8位数的减法。 8.1.3 arm_abs_q15 这个函数用于求15位定点数的绝对值,源代码分析如下: - /**
- * @brief Q15 vector absolute value.
- * @param[in] *pSrc points to the input buffer
- * @param[out] *pDst points to the output buffer
- * @param[in] blockSize number of samples in each vector
- * @return none.
- *
- * <b>Scaling and Overflow Behavior:</b>
- * \par
- * The function uses saturating arithmetic.
- * The Q15 value -1 (0x8000) will be saturated to the maximum allowable positive value 0x7FFF. (1)
- */
-
- void arm_abs_q15(
- q15_t * pSrc,
- q15_t * pDst,
- uint32_t blockSize)
- {
- uint32_t blkCnt; /* loop counter */
-
- #ifndef ARM_MATH_CM0_FAMILY
- __SIMD32_TYPE *simd; (2)
-
- /* Run the below code for Cortex-M4 and Cortex-M3 */
-
- q15_t in1; /* Input value1 */
- q15_t in2; /* Input value2 */
-
-
- /*loop Unrolling */
- blkCnt = blockSize >> 2u;
-
- /* First part of the processing with loop unrolling. Compute 4 outputs at a time.
- ** a second loop below computes the remaining 1 to 3 samples. */
- simd = __SIMD32_CONST(pDst); (3)
- while(blkCnt > 0u)
- {
- /* C = |A| */
- /* Read two inputs */
- in1 = *pSrc++;
- in2 = *pSrc++;
-
-
- /* Store the Absolute result in the destination buffer by packing the two values, in a single cycle */
- #ifndef ARM_MATH_BIG_ENDIAN
- *simd++ =
- __PKHBT(((in1 > 0) ? in1 : (q15_t)__QSUB16(0, in1)), (4)
- ((in2 > 0) ? in2 : (q15_t)__QSUB16(0, in2)), 16);
-
- #else
-
-
- *simd++ =
- __PKHBT(((in2 > 0) ? in2 : (q15_t)__QSUB16(0, in2)),
- ((in1 > 0) ? in1 : (q15_t)__QSUB16(0, in1)), 16);
-
- #endif /* #ifndef ARM_MATH_BIG_ENDIAN */
-
- in1 = *pSrc++;
- in2 = *pSrc++;
-
-
- #ifndef ARM_MATH_BIG_ENDIAN
-
- *simd++ =
- __PKHBT(((in1 > 0) ? in1 : (q15_t)__QSUB16(0, in1)),
- ((in2 > 0) ? in2 : (q15_t)__QSUB16(0, in2)), 16);
-
- #else
-
-
- *simd++ =
- __PKHBT(((in2 > 0) ? in2 : (q15_t)__QSUB16(0, in2)),
- ((in1 > 0) ? in1 : (q15_t)__QSUB16(0, in1)), 16);
-
- #endif /* #ifndef ARM_MATH_BIG_ENDIAN */
-
- /* Decrement the loop counter */
- blkCnt--;
- }
- pDst = (q15_t *)simd;
- /* If the blockSize is not a multiple of 4, compute any remaining output samples here.
- ** No loop unrolling is used. */
- blkCnt = blockSize % 0x4u;
-
- while(blkCnt > 0u)
- {
- /* C = |A| */
- /* Read the input */
- in1 = *pSrc++;
-
- /* Calculate absolute value of input and then store the result in the destination buffer. */
- *pDst++ = (in1 > 0) ? in1 : (q15_t)__QSUB16(0, in1);
-
- /* Decrement the loop counter */
- blkCnt--;
- }
-
- #else
-
- /* Run the below code for Cortex-M0 */
-
- q15_t in; /* Temporary input variable */
-
- /* Initialize blkCnt with number of samples */
- blkCnt = blockSize;
-
- while(blkCnt > 0u)
- {
- /* C = |A| */
- /* Read the input */
- in = *pSrc++;
-
- /* Calculate absolute value of input and then store the result in the destination buffer. */
- *pDst++ = (in > 0) ? in : ((in == (q15_t) 0x8000) ? 0x7fff : -in);
-
- /* Decrement the loop counter */
- blkCnt--;
- }
-
- #endif /* #ifndef ARM_MATH_CM0_FAMILY */
-
- }
1. 对于Q15格式的数据,饱和运算会使得数据0x8000变成0x7fff。 2. __SIMD32_TYPE的定义在文件arm_math.h中,具体定义如下: #define __SIMD32_TYPE int32_t __packed SIMD就是咱们上期教程所将的单指令多数据流。简单的理解就是__SIMD32_TYPE就是定义了一个int32_t类型的数据,__packed的含义就是实现字节的对齐功能,方便两个16位数据的都存入到这个数据类型中。 3. 函数__SIMD32_CONST的定义如下: #define __SIMD32_CONST(addr) ((__SIMD32_TYPE *)(addr)) 4. 函数__PKHBT的定义在文件core_cm4_simd.h,定义如下: #define __PKHBT(ARG1,ARG2,ARG3) ( ((((uint32_t)(ARG1)) ) & 0x0000FFFFUL) | \ ((((uint32_t)(ARG2)) << (ARG3)) & 0xFFFF0000UL) ) 这个宏定义的作用就是将将两个16位的数据合并成32位数据。但是有一点要特别说明__PKHBT也是CM4内核支持的SIMD指令,上面的宏定义的C函数会被MDK自动识别并调用相应的PKHBT指令。 __QSUB16用于实现16位数据的饱和减法。 8.1.4 arm_abs_q7 这个函数用于求8位定点数的绝对值,源代码分析如下: - /**
- * @brief Q7 vector absolute value.
- * @param[in] *pSrc points to the input buffer
- * @param[out] *pDst points to the output buffer
- * @param[in] blockSize number of samples in each vector
- * @return none.
- *
- * \par Conditions for optimum performance
- * Input and output buffers should be aligned by 32-bit
- *
- *
- * <b>Scaling and Overflow Behavior:</b> (1)
- * \par
- * The function uses saturating arithmetic.
- * The Q7 value -1 (0x80) will be saturated to the maximum allowable positive value 0x7F.
- */
-
- void arm_abs_q7(
- q7_t * pSrc,
- q7_t * pDst,
- uint32_t blockSize)
- {
- uint32_t blkCnt; /* loop counter */
- q7_t in; /* Input value1 */
-
- #ifndef ARM_MATH_CM0_FAMILY
-
- /* Run the below code for Cortex-M4 and Cortex-M3 */
- q31_t in1, in2, in3, in4; /* temporary input variables */
- q31_t out1, out2, out3, out4; /* temporary output variables */
-
- /*loop Unrolling */
- blkCnt = blockSize >> 2u;
-
- /* First part of the processing with loop unrolling. Compute 4 outputs at a time.
- ** a second loop below computes the remaining 1 to 3 samples. */
- while(blkCnt > 0u)
- {
- /* C = |A| */
- /* Read inputs */
- in1 = (q31_t) * pSrc;
- in2 = (q31_t) * (pSrc + 1);
- in3 = (q31_t) * (pSrc + 2);
-
- /* find absolute value */
- out1 = (in1 > 0) ? in1 : (q31_t)__QSUB8(0, in1); (2)
-
- /* read input */
- in4 = (q31_t) * (pSrc + 3);
-
- /* find absolute value */
- out2 = (in2 > 0) ? in2 : (q31_t)__QSUB8(0, in2);
-
- /* store result to destination */
- *pDst = (q7_t) out1;
-
- /* find absolute value */
- out3 = (in3 > 0) ? in3 : (q31_t)__QSUB8(0, in3);
-
- /* find absolute value */
- out4 = (in4 > 0) ? in4 : (q31_t)__QSUB8(0, in4);
-
- /* store result to destination */
- *(pDst + 1) = (q7_t) out2;
-
- /* store result to destination */
- *(pDst + 2) = (q7_t) out3;
-
- /* store result to destination */
- *(pDst + 3) = (q7_t) out4;
-
- /* update pointers to process next samples */
- pSrc += 4u;
- pDst += 4u;
-
- /* Decrement the loop counter */
- blkCnt--;
- }
-
- /* If the blockSize is not a multiple of 4, compute any remaining output samples here.
- ** No loop unrolling is used. */
- blkCnt = blockSize % 0x4u;
- #else
-
- /* Run the below code for Cortex-M0 */
- blkCnt = blockSize;
-
- #endif // #define ARM_MATH_CM0_FAMILY
-
- while(blkCnt > 0u)
- {
- /* C = |A| */
- /* Read the input */
- in = *pSrc++;
-
- /* Store the Absolute result in the destination buffer */
- *pDst++ = (in > 0) ? in : ((in == (q7_t) 0x80) ? 0x7f : -in);
-
- /* Decrement the loop counter */
- blkCnt--;
- }
- }
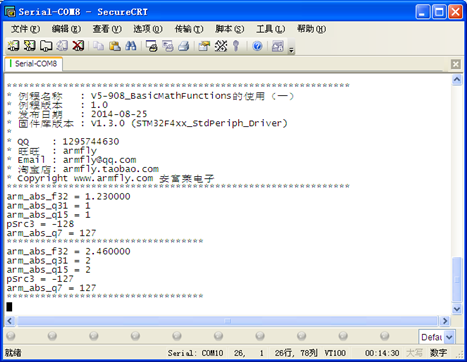
1. 由于饱和运算,0x80求绝对值将变成数据0x7F。 2. __QSUB8用以实现8位数的饱和减法运算。 8.1.5 实例讲解实验目的: 1. 四种数据类型数据绝对值求解 实验内容: 1. 按下按键K1, 串口打印输出结果 实验现象: 通过窗口上位机软件SecureCRT(V5光盘里面有此软件)查看打印信息现象如下: 程序设计: - /*
- *********************************************************************************************************
- * 函 数 名: DSP_ABS
- * 功能说明: 求绝对值
- * 形 参:无
- * 返 回 值: 无
- *********************************************************************************************************
- */
- static void DSP_ABS(void)
- {
- static float32_t pSrc;
- static float32_t pDst;
- static q31_t pSrc1;
- static q31_t pDst1;
- static q15_t pSrc2;
- static q15_t pDst2;
- static q7_t pSrc3 = 127; /* 为了说明问题,在这里设置初始值为127,然后查看0x80是否饱和为0x7F */
- static q7_t pDst3;
- pSrc -= 1.23f;
- arm_abs_f32(&pSrc, &pDst, 1); (1)
- printf("arm_abs_f32 = %f\r\n", pDst);
-
- pSrc1 -= 1;
- arm_abs_q31(&pSrc1, &pDst1, 1); (2)
- printf("arm_abs_q31 = %d\r\n", pDst1);
-
- pSrc2 -= 1;
- arm_abs_q15(&pSrc2, &pDst2, 1); (3)
- printf("arm_abs_q15 = %d\r\n", pDst2);
-
- pSrc3 += 1;
- printf("pSrc3 = %d\r\n", pSrc3);
- arm_abs_q7(&pSrc3, &pDst3, 1); (4)
- printf("arm_abs_q7 = %d\r\n", pDst3);
- printf("***********************************\r\n");
- }
(1)到(4)实现相应格式下绝对值的求解。这里只求了一个数,大家可以尝试求解一个数组的绝对值。
| 
 微信公众号
微信公众号
 手机版
手机版

8.5 总结