
|
在昨天的文章里面,我们给大家简单的分享了关于c++里面的函数模板的概念,通过代码示例,我们对函数模板的优势有了一个比较清楚的认识。咋们今天继续来深入学习函数模板。以下内容是今天知识学习总结笔记。 一、函数模板的深入理解: 1、函数模板深入理解:
-对模板代码本身进行编译,比如检查函数模板是否有语法上的错误 -对参数替换后的代码进行编译;也就是说,我们在调用函数模板的时候,编译器根据实际的参数类型,从而得到真正的函数,这个时候编译器会对这个函数进行第二次编译 2、注意事项:
-自动推导类型时,必须严格匹配 -显示类型指定时,能够进行隐式类型转换 代码实践: 代码版本一: #include <iostream>#include <string> using namespace std; class Test { Test(const Test&); public: Test() { } }; template < typename T > void Swap(T& a, T& b) { T c = a; a = b; a = c; } typedef void(fun1)(int&, int&); typedef void(fun2)(double&, double&); typedef void(fun3)(Test&,Test&); int main() { /* p1 和 p2 指向具体函数,但是 p1 和 p2 指向的具体函数是由函数模板具体产生,这里已经产生了函数,不是模板了,这两个函数是两个独立的不同的函数,我们通过函数打印地址,就能够明显发现 */ fun1 *p1 = Swap; // 定义函数指针,并能编译通过;这里编译器通过函数指针的类型自动推导 T 为 int; 编译器默默做的事有:1、首先进行自动推导;2、产生真正的 Swap() 函数;3、将实际生成的 Swap() 函数地址用于初始化 pi; fun2 *p2 = Swap;//编译器自动推导为double cout<<"p1 ="<<reinterpret_cast<void*>(p1)<<endl;//// 将 p1 这个指针的类型重解释为 void* cout<<"p2 ="<<reinterpret_cast<void*>(p2)<<endl; return 0; } 输出结果: root@txp-virtual-machine:/home/txp# ./a.outp1 =0x400964 p2 =0x400990 代码版本二: #include <iostream>#include <string> using namespace std; class Test { Test(const Test&); public: Test() { } }; template < typename T > void Swap(T& a, T& b) { T c = a; a = b; a = c; } typedef void(fun1)(int&, int&); typedef void(fun2)(double&, double&); typedef void(fun3)(Test&,Test&); int main() { fun1 *p1 = Swap; fun2 *p2 = Swap; fun3 *p3 = Swap; cout<<"p1 ="<<reinterpret_cast<void*>(p1)<<endl; cout<<"p2 ="<<reinterpret_cast<void*>(p2)<<endl; cout<<"p3 ="<<reinterpret_cast<void*>(p3)<<endl; return 0; } 输出结果: root@txp-virtual-machine:/home/txp# g++ test.cpptest.cpp: In instantiation of ‘void Swap(T&, T&) [with T = Test]’: test.cpp:32:16: required from here test.cpp:8:6: error: ‘Test::Test(const Test&)’ is private Test(const Test&); ^ test.cpp:19:11: error: within this context T c = a; ^ 注解:显示编译器自动推导T为Test类,也就是Swap(T&,T&),然后就报了一个错误,说拷贝构造函数是私密的,所以也就导致Test c =a这里报错了 3、多参数函数模板 (1)函数模板可以定义任意多个不同的类型参数 template < typename T1, typename T2, typename T3 >T1 Add(T2 a, T3 b) { return static_cast<T1>(a+b); } (2)对于多参数函数模板
int r1 =Add<int>(0.5,0.8); //T1 = int, T2 = float, T3 = double int r2 =Add<int,float>(0.5,0.8); //T1 = int, T2 = float, T3 = float int r3 =Add<int,float,float>(0.5,0.8); 注:工程中将返回值参数作为第一个类型参数 代码实践: #include <iostream>#include <string> using namespace std; template < typename T1, typename T2, typename T3 > T1 Add(T2 a, T3 b) { return static_cast<T1>(a + b); } int main() { // T1 = int, T2 = double, T3 = double int r1 = Add<int>(0.5, 0.8); // T1 = double, T2 = float, T3 = double double r2 = Add<double, float>(0.5, 0.8); // T1 = float, T2 = float, T3 = float float r3 = Add<float, float, float>(0.5, 0.8); cout << "r1 = " << r1 << endl; // r1 = 1 cout << "r2 = " << r2 << endl; // r2 = 1.3 cout << "r3 = " << r3 << endl; // r3 = 1.3 return 0; } 输出结果: root@txp-virtual-machine:/home/txp# ./a.outr1 = 1 r2 = 1.3 r3 = 1.3 4、当函数重载遇到函数模板会发生什么? (1)函数模板可以像普通函数一样被重载
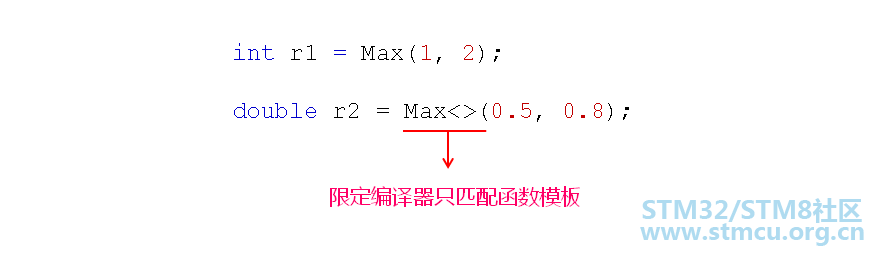
代码实践: #include <iostream>#include <string> using namespace std; template < typename T > T Max(T a, T b) { cout << "T Max(T a, T b)" << endl; return a > b ? a : b; } int Max(int a, int b) { cout << "int Max(int a, int b)" << endl; return a > b ? a : b; } template < typename T > T Max(T a, T b, T c) { cout << "T Max(T a, T b, T c)" << endl; return Max(Max(a, b), c); } int main() { int a = 1; int b = 2; cout << Max(a, b) << endl; // 普通函数 Max(int, int) cout << Max<>(a, b) << endl; // 函数模板 Max<int>(int, int) cout << Max(3.0, 4.0) << endl; // 函数模板 Max<double>(double, double) cout << Max(5.0, 6.0, 7.0) << endl; // 函数模板 Max<double>(double, double, double) cout << Max('a', 100) << endl; // 普通函数 Max(int, int) return 0; } 输出结果: root@txp-virtual-machine:/home/txp# ./a.outint Max(int a, int b) 2 T Max(T a, T b) 2 T Max(T a, T b) 4 I Max(T a, T b, T c) T Max(T a, T b) T Max(T a, T b) 7 int Max(int a, int b) 100 二、总结:
好了,今天的分享就到这里,如果文章中有错误或者不理解的地方,可以交流互动,一起进步。 |
| 学习了 |
 微信公众号
微信公众号
 手机版
手机版
