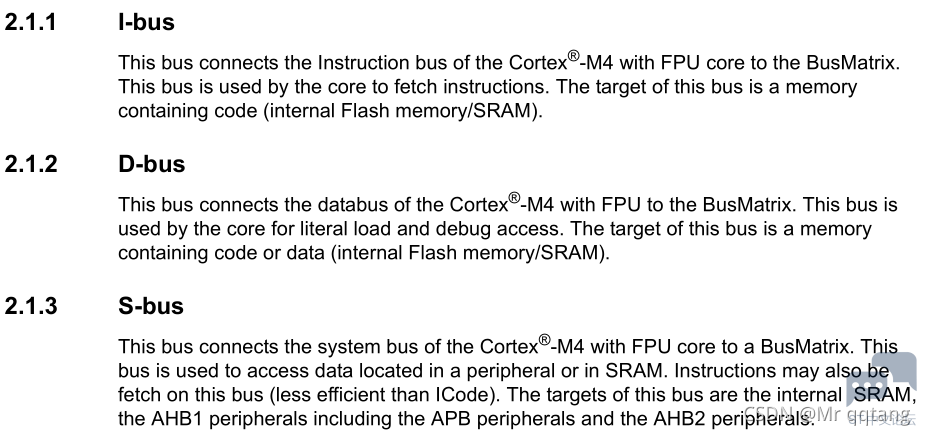
In order to run codes in RAM space, the I-Bus of the CPU must have the access to the RAM address. Take STM32F401 MCU as an example, it has a Cortex-M4 CPU which has three buses, I-bus, D-bus and S-bus, the purposes of each bus are explained in the reference manual RM0368 as below.
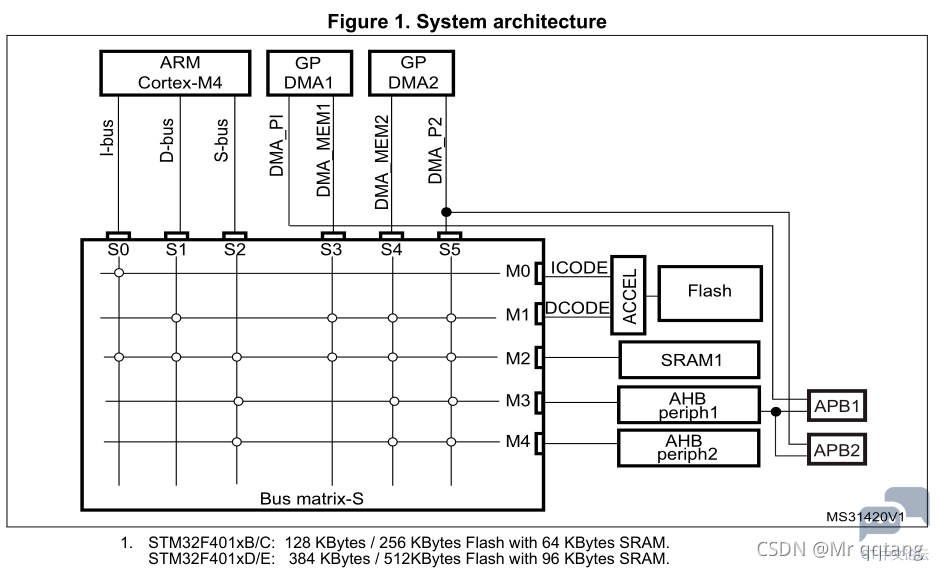
It clearly says that I-bus can access internal Flash memory and SRAM, therefore, we can set the PC(R15) register to the RAM address space to run codes in SRAM. Also, we can see from the bus matrix of STM32F401 as below that I-bus can only access Flash and SRAM while AHB peripherals are inaccessible. Apart from that, S-bus can also be used to fetch instructions both from SRAM and AHB peripherals like FSMC which is used to control external Nor-flash, Nand-flash and SRAM/SDRAM.
It is worth mentioning that the I-bus of ESP32 can only access Internal SRAM 1. What's worse, I-bus can access Internal SRAM 1(0x3FFE0000 ~ 0x3FFFFFFF) through 0x400A0000 ~ 0x400BFFFF, and the mapping relationship is inverted, for instance, visiting 0x3FFE0000 and 0x400BFFFC gets the same result.
Test codes:
- #include <stm32f10x_conf.h>
- #include "sys.h"
- #include "delay.h"
- #include "usart.h"
- #include "string.h"
-
- __align(8) uint8_t value[1024] __attribute__((at(0x20000100)));
-
- void UartSendByte(USART_TypeDef* uart,u8 data);
-
- void test(void (*p)(USART_TypeDef*,u8))
- {
- p(USART1, ((unsigned int)test >> 24) & 0xFF);
- p(USART1, ((unsigned int)test >> 16) & 0xFF);
- p(USART1, ((unsigned int)test >> 8) & 0xFF);
- p(USART1, ((unsigned int)test >> 0) & 0xFF);
- }
-
- void Initialization()
- {
- MCU_INIT(RCC_PLLMul_9);
- Uart_Init(USART1,115200,72);
- }
-
- int main(void)
- {
- Initialization();
-
- printf("%.8X\r\n", (unsigned int)main);
-
- unsigned int addr = (unsigned int)test & 0xFFFFFFFE; //最低位置1表示Thumb模式,清空该位为函数实际地址
- printf("%.8X\r\n", addr);
-
- memcpy(value, (uint8_t *)addr, sizeof(value));
-
- void (*p)(void*) = (void (*)(void*))((unsigned int)(value) | 0x01); //最低位置1进入Thumb模式
- printf("%.8X\r\n", p);
- p(UartSendByte);
-
- while(1);
- }
-
-
由于代码中很多函数的跳转都是相对跳转,所以,如果在test函数中直接调用UartSendByte函数,那么直接调用test函数是没有问题的,但是将test函数拷贝到内存中去再执行,相对跳转的地址就不对了。所以测试函数里面使用函数指针将UartSendByte函数的地址做为参数传入到test中。
也可以将代码保存在一个const类型的常量数组里面,然后执行这个数组(注意跳转到thumb代码的话要将PC指针的最低位置1,并且拷贝函数的内容的时候也要注意获取到的函数地址的最低位是置1的,拷贝时要清零,不然会少拷贝一个字节)。如下代码:
- // 定义一个常量数组,注意需要4字节对齐
- const unsigned char subapp[5 * 1024] __attribute__((aligned(8))) =
- {
- 0x64, 0x30, 0x70, 0x47, 0x70, 0xB5, 0x04, 0x29,
- 0xAD, 0xF5, 0x00, 0x6D, 0x49, 0xD0, 0x06, 0x29,
- 0x44, 0xD1, 0xF3, 0xA0, 0xE9, 0xF5, 0xDC, 0xE6,
- 0x00, 0x24, 0x6D, 0x46, 0xAF, 0xF2, 0x1D, 0x06,
- 0x33, 0x5D, 0x07, 0x21, 0xF8, 0xA2, 0x28, 0x46,
- 0x4F, 0xF6, 0x85, 0xF7, 0x64, 0x1C, 0xAD, 0x1D,
- 0x80, 0x2C, 0xF5, 0xD3, 0x68, 0x46, 0x95, 0xF7,
- 0x22, 0xFF, 0xE1, 0x49, 0x6F, 0x24, 0xF8, 0x22,
- 0x20, 0x31, 0xF3, 0xA3, 0xE0, 0xA0, 0xFF, 0xF7,
- 0xB4, 0xFF, 0xF3, 0xA0, 0x21, 0x46, 0xFF, 0xF7,
- 0xB0, 0xFF, 0xDB, 0x49, 0xFB, 0x22, 0xF2, 0x4C,
- 0xEE, 0xA3, 0x20, 0x31, 0xDA, 0xA0, 0xFF, 0xF7,
- 0xA8, 0xFF, 0x61, 0x1E, 0xF0, 0xA0, 0xFF, 0xF7,
- 0xA4, 0xFF, 0xD5, 0x49, 0xFC, 0x22, 0xE8, 0xA3,
- 0x20, 0x31, 0xD4, 0xA0, 0xFF, 0xF7, 0x9D, 0xFF,
- 0xEB, 0xA0, 0x21, 0x46, 0xFF, 0xF7, 0x99, 0xFF,
- };
-
- // 这个函数就是要被拷贝的函数,内容就存在了上面的常量数组里面,注意不要调用别的函数,因为可能是相对寻址,拷贝之后,代码位置改变了,相对位置不一致了
- int mytest(int n)
- {
- return n + 100;
- }
-
- int main(void)
- {
- // 将mytest函数的内容以hex方式打印出来,因为不知道mytest多长,所以多打印一些,打印出来的数据填入到subapp数组
- LOGI("mytest", "%.8X", (unsigned int)mytest); // print the address of mytest, be aware of the last bit of the address is set which indicates it's thumb code
- unsigned int i;
- char buff[2048];
- char *pbuff = buff;
- for (i = 0; i < 128; i++) {
- snprintf(pbuff, 7, "0x%.2X, ", *((unsigned char*)((unsigned int)mytest & (~0x01)) + i)); // 注意mytest的值的最后一位被置1了,表示thumb code,拷贝的时候需要清除
- pbuff += 6;
- }
- duer_print_long_msg(buff);
-
- int n = mytest(11);
- LOGI("subapp", "n:%d", n);
-
- int (*p)(int) = (int (*)(int))((unsigned int)subapp | 0x01); // 最后一位需要置1,表示thumb code
- LOGI("subapp", "%.8X", (unsigned int)subapp);
- LOGI("subapp", "%.8X", (unsigned int)p);
- n = p(66);
- LOGI("subapp", "start:%d", n);
-
- return 0;
-
- }
————————————————
版权声明:哐哐哐 Quan
如有侵权请联系删除
|



 微信公众号
微信公众号
 手机版
手机版
