
.png) STMCU小助手
发布时间:2021-12-18 17:43
STMCU小助手
发布时间:2021-12-18 17:43
|
printf重定向介绍 在学C语言的时候,会经常用标准库<stdio.h>中printf(), scanf()这两个函数, 来实现数据的输入与输出. 格式化输入输出的功能还是挺强大的, 那已经有了现成的轮子, 就要寻思一下如何进一步在单片机上使用它. 下面是ARM Compiler6文档中对printf的介绍: The printf family consists of _printf(), printf(), _fprintf(), fprintf(), vprintf(), and vfprintf(). All these functions use __FILE opaquely and depend only on the functions fputc() and ferror(). The functions _printf() and _fprintf() are identical to printf() and fprintf() except that they cannot format floating-point values. The standard output functions of the form _printf(…) are equivalent to: fprintf(& __stdout, …)where __stdout has type __FILE. 大致是说printf家族有这么些函数<_printf(), printf(), _fprintf(), fprintf(), vprintf(), and vfprintf()>, 这些函数都隐式的使用__FILE<文件流>, 并且只依靠fputc(), ferror()这两个函数. If you define your own version of __FILE, your own fputc() and ferror() functions, and the __stdout object, you can use all of the printf() family, fwrite(), fputs(), puts() and the C++ object std::cout unchanged from the library. 重新定义__FILE, fputc(), ferror(), __stdout, 就可以使用printf()家族的各种函数了. STM32中printf重定向 下面是官方给出的重映射模板: <遇到不会的先看看文档往往能得到最直接的答案>
要将printf()重定向到STM32中的串口, 只需要重新实现 fputc() 函数即可, 在fputc()中通过串口发送一个char. 在上一次的工程上进行修改, 将printf()重定向到串口3.
写个简单的程序试一试:
输出结果: 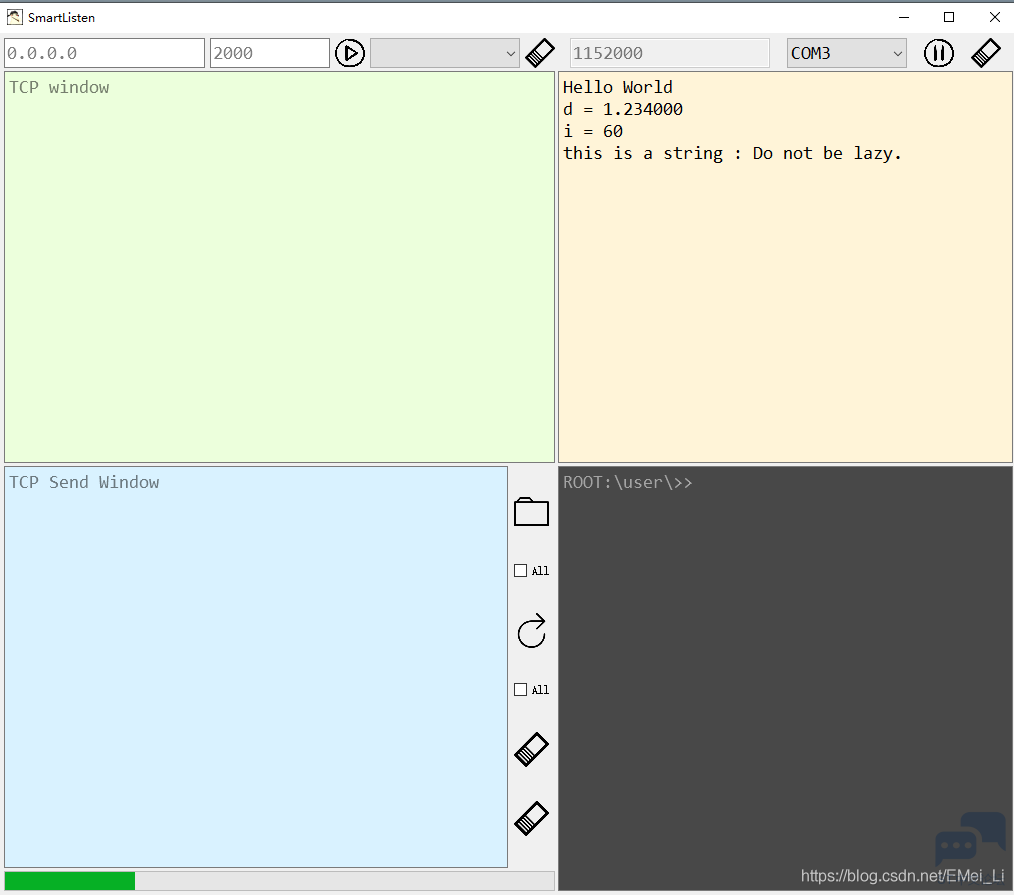
可以开始愉快的使用printf()了. |
STM32和Arduino对比,谁更耐打?
STM32 LL为什么比HAL高效?
STM32H7 SPI Underrun 特性实战指南:配置、行为与传输可靠性优化
【STM32H750-DK 车辆仪表】6.模拟温度和胎压监测
【STM32H750-DK 车辆仪表】5.油表
【STM32H750-DK 车辆仪表】4.仪表时钟
【STM32H750-DK 车辆仪表】3.车速控制UI
【STM32H750-DK 车辆仪表】2.与板卡交互
【STM32H750-DK 车辆仪表】1.灯光控制UI
STM32应用过程中与电源相关的案例分享
 微信公众号
微信公众号
 手机版
手机版
